Peer-Reviewed Article · Jun 25, 2024
Communicating the links between climate change and heat waves with the Climate Shift Index
By Laura Thomas-Walters, Matthew Goldberg, Sanguk Lee, Aidan Lyde, Seth Rosenthal and Anthony Leiserowitz
Filed under: Messaging

We are pleased to announce the publication of a new article, “Communicating the links between climate change and heat waves with the Climate Shift Index” in the journal Weather, Climate, and Society.
Extreme weather, including heat waves, poses a significant threat to human health and ecosystems. As global temperatures continue to rise, heat waves are becoming more frequent and severe. Because of this, communicating heat-related risks to the public is increasingly important for both their own protection and to encourage mitigation policies.
We conducted a message experiment with 3,902 Americans, focused on the July 2023 heat wave that occurred in much of the United States. We used Climate Central’s Climate Shift Index (CSI), which calculates how much more likely a heat wave was made by climate change. We informed study participants that climate change made the July 2023 heat wave at least 5 times more likely (see Figure 1). We also explored other potential messages, such as reframing magnitude as a percentage (i.e., “400% more likely”), and whether adding different explanations of the relationship between climate change and heat waves further increase understanding.
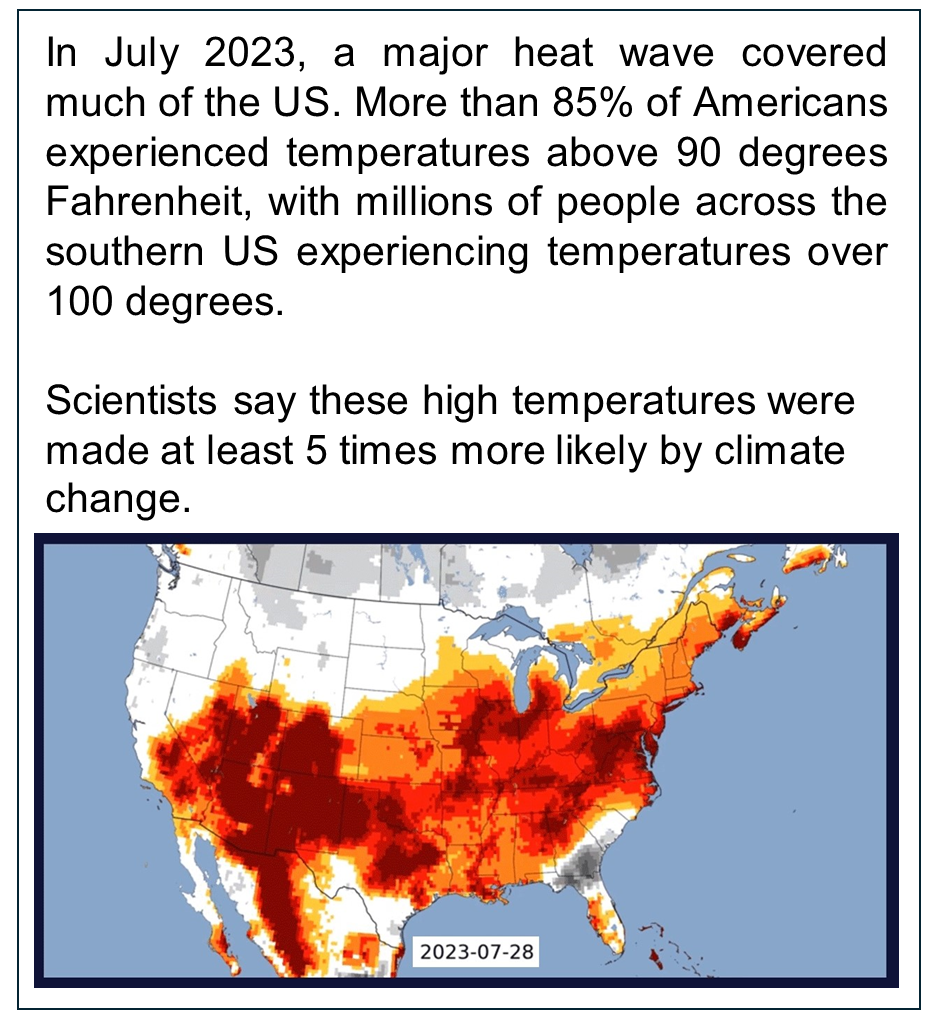
We found that prior to exposure to the attribution message, a majority of research participants thought climate change made the July 2023 heat wave more likely (53%), and that it is making heat waves generally more likely (58%). All messages then increased the belief that climate change made the July 2023 heat wave more likely (see Figure 2) and is making heat waves in general more likely as well. Expressing the magnitude as a percentage was more effective than the standard CSI framing, leading to a 6 percentage point increase in the belief that climate change made the July 2023 heat wave more likely, compared to a “pure control” message (i.e., a message unrelated to climate change and extreme weather), or a 1 percentage point increase compared to the standard CSI treatment. We also found that just talking about the heat wave, without mentioning climate change (what we call the “Active Control” in Figure 2), was itself enough to significantly change beliefs.
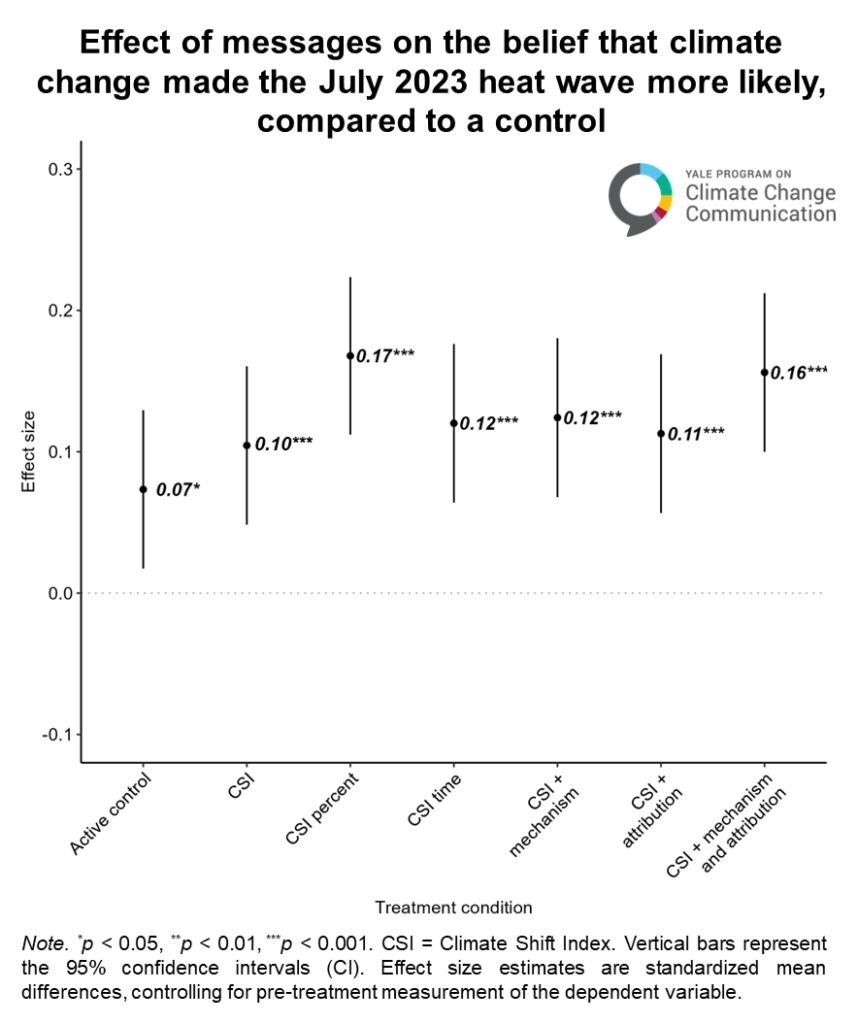
The full paper includes many other important results, including the impact of the different messages on beliefs that climate change is making heat waves in the US more likely and worse, support for government action, and how responses differed across different demographic groups, including Global Warming’s Six Americas.
The full article with many other results is available Open Access here at Weather, Climate and Society.
The research team is grateful for valuable input from Andy Pershing and his colleagues at Climate Central.